SYNTHESIS OF 4-CHLORO-1-{[5-(4-NITROPHENYL)-1,3,4-OXADIAZOL-2-YL]METHYL}QUINOLIN-2(1<i>H</i>)-ONE AND <i>N</i>'-[2-(4-METHYL-2-OXOQUINOLIN-1(2<i>H</i>)-YL)ACETYL]-4-NITROBENZOHYDRAZIDE USING POCl<sub>3</sub> AND THEIR CYTOTOXIC ACTIVITY AGAINST HUMAN LUNG CANCER CELLS A549
Keywords:
4-chloroquinolinehydrazide, 4-methylquinolinehydrazide, POCl3, quinolin-2(1H)-one, cyclodehydration, cytotoxicity, human lung cancer cells A549Abstract
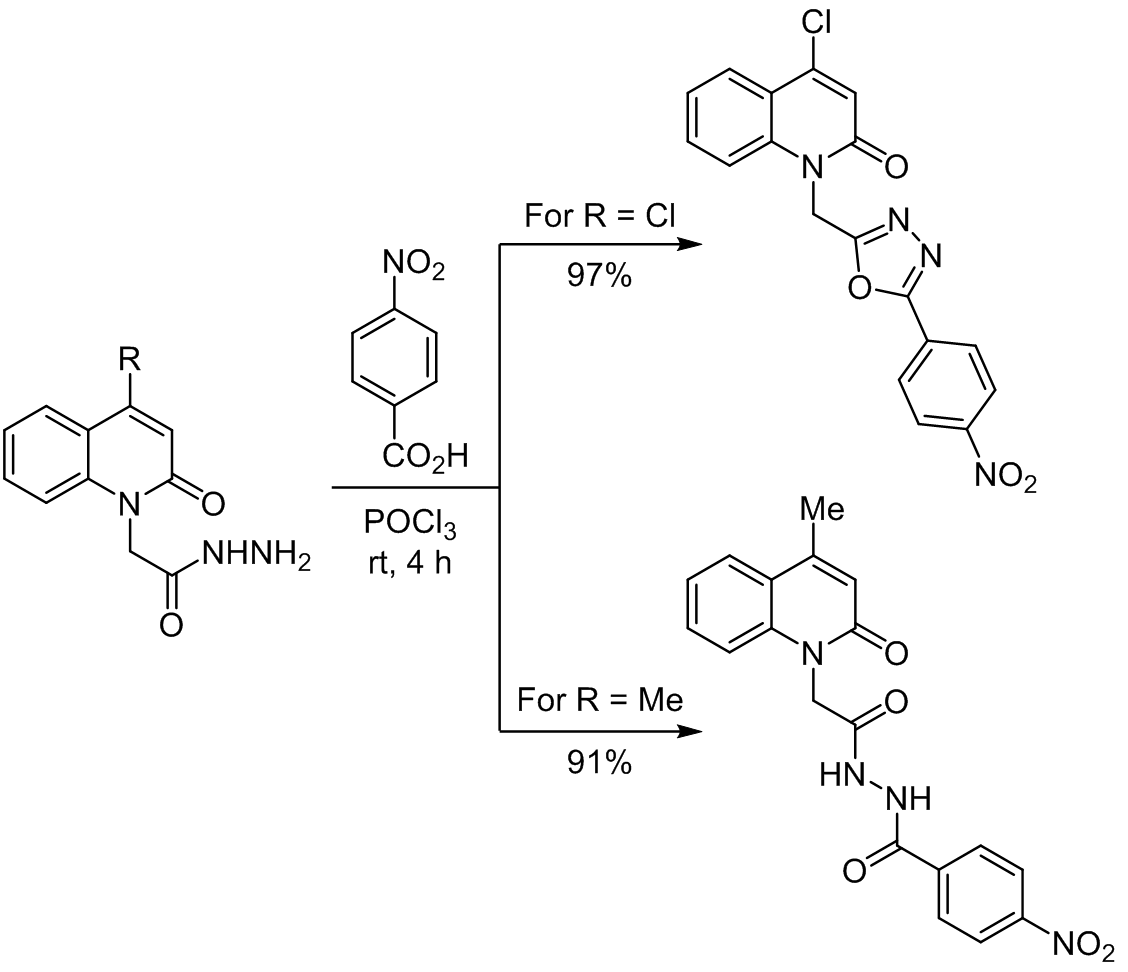
We have studied POCl3-catalyzed cyclodehydration reaction of 2-(4-chloro-2-oxoquinolin-1(2H)-yl)acetohydrazide with benzoic acids. Unusually, we have found that p-methyl-, p-methoxy-, p-chloro-substituted and unsubstituted benzoic acids failed to undergo cyclodehydration, and were converted into the corresponding anhydrides. Whereas, p-nitrobenzoic acid successfully underwent cyclodehydration and yielded 1,3,4-oxadiazole. Trying the same reaction with 2-(4-methyl-2-oxoquinolin-1(2H)-yl)-acetohydrazide and p-nitrobenzoic acid, there was no cyclodehydration – two hydrazide molecules have condensed together. Newly synthesized 4-chloro-1{[5-(4-nitrophenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl]methyl}quinolin-2(1H)-one and N'-[2-(4-methyl-2-oxoquinolin-1(2H)-yl)acetyl]-4-nitrobenzohydrazide were evaluated for their anticancer activity against human lung cancer cells A549.