UNEXPECTED PRODUCTS OF THE REACTION OF PURINE NUCLEIC BASE PERCHLORATES WITH ACETYLACETONE CAUSING SINGLE-STRAND BREAKS IN THE DNA MOLECULE
Keywords:
DNA, guanine, perchlorate, purines, ring opening, single-strand breaks, adenineAbstract
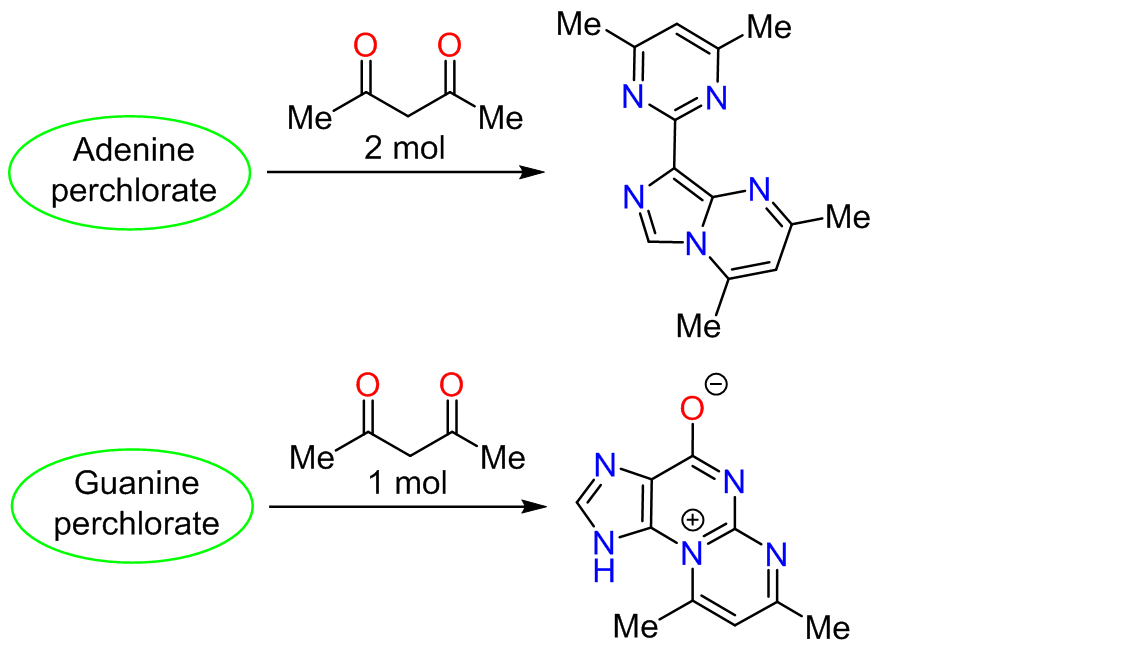
The reactions of purine nucleic base perchlorates with the simplest 1,3-diketone – acetylacetone – were studied for the first time. It was demonstrated that adenine reacts with acetylacetone in a 1:2 molar ratio via opening of the pyrimidine fragment of the bicyclic structure, elimination of a one-carbon fragment in the form of a formic acid molecule, and recyclization into 8-(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)-2,4-dimethylimidazo[1,5-a]pyrimidine. Guanine, in turn, reacted with acetylacetone in a 1:1 ratio and formed 7,9-dimethyl-3H-pyrimido-[2,1-b]purin-10-ium-4-olate. In this case, the direction of heterocyclization differed from that observed in the reaction of guanine with malondialdehyde during the in vitro and in vivo formation of the minor nucleotide base M1G. The synthesized compounds were capable of causing single-strand breaks in DNA macromolecules.