A computational exploration of the antioxidant potential of conjugated quinazolinone Schiff bases
Ключевые слова:
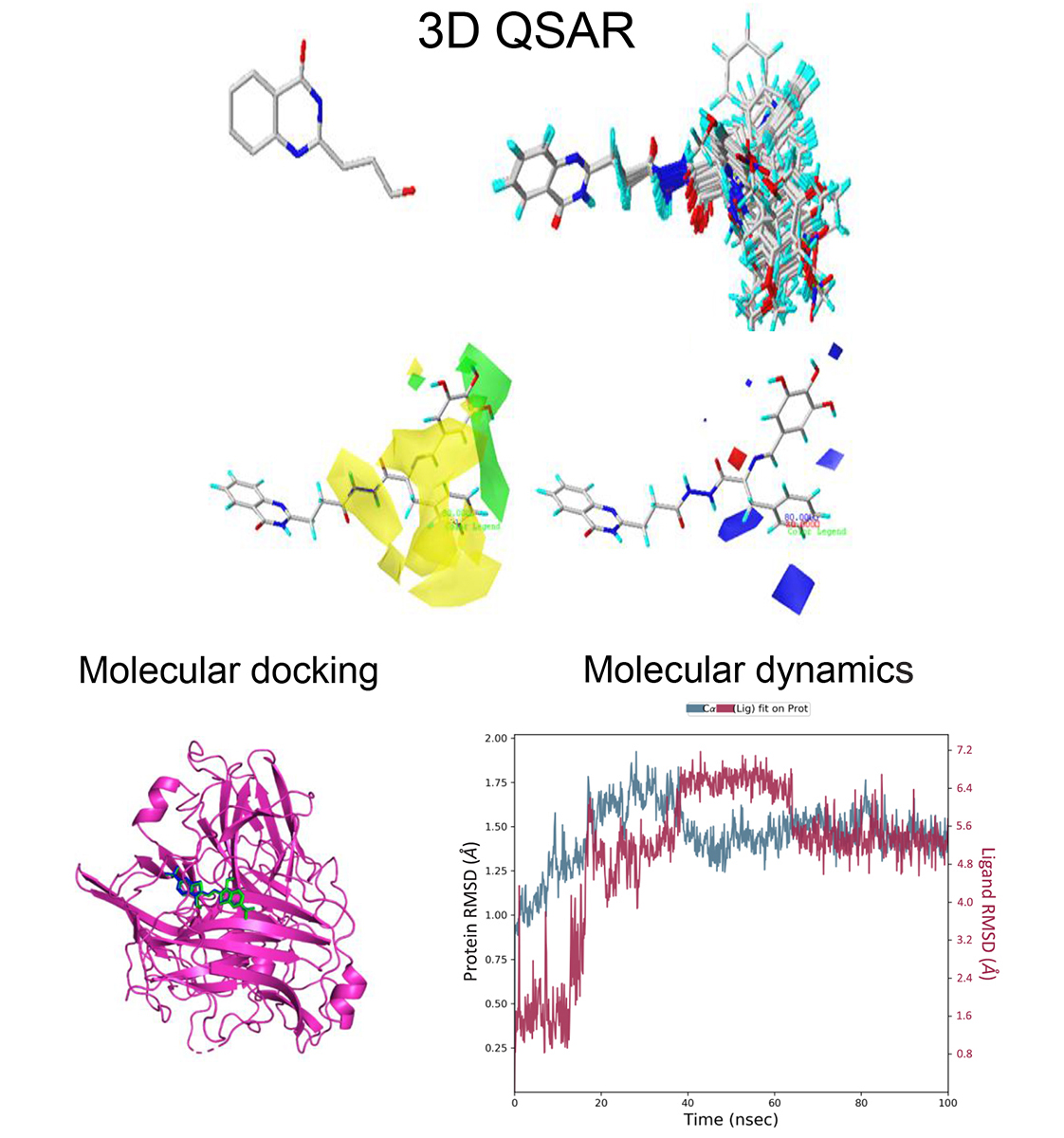
Quinazolinone, Antioxidant, 3D-QSAR, Molecular Docking, ADMETАннотация
The antioxidant properties of quinazolinone are essential in preventing free radicals from damaging human tissue by inhibiting and slowing lipid oxidation. The study results indicate that the comparative molecular similarity indices analysis (CoMSIA) model outperforms the comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA) and hologram quantitative structure–activity relationship (HQSAR) models. The CoMSIA model, selected for this study, combines structural, electrostatic, hydrophobic, and donor properties. The model produced a correlation coefficient of 0.85, a cross-validated correlation coefficient of 0.982, a standard error of estimation of 0.059, and an F value of 280.660. Based on the results obtained from the contour plot, three compounds with potent predicted antioxidant activity have been proposed. The study involved an evaluation of various compounds using molecular docking. The results showed that one of the molecules had favorable interactions with its target receptor with high-affinity energies. Molecular dynamic simulations were performed to validate docking results, and findings can be used to guide the design of antioxidant compounds. Furthermore, ADMET properties of the newly developed compounds were also evaluated in silico, and three derivatives met the properties. These results will provide valuable information for the design of antioxidant compounds.