Quantum evaluation of novel epoxides: molecular docking, dynamics simulation, pharmacokinetics, stereoselectivity, and mechanistic insights into <i>cis</i>-himachalone and <i>cis</i>-himachalol epoxidation
Ключевые слова:
Epoxidation, DFT reactivity indices, S. aureus topoisomerase IV, Docking, Molecular dynamic, Cis-himachlone, Cis-himachalol.Аннотация
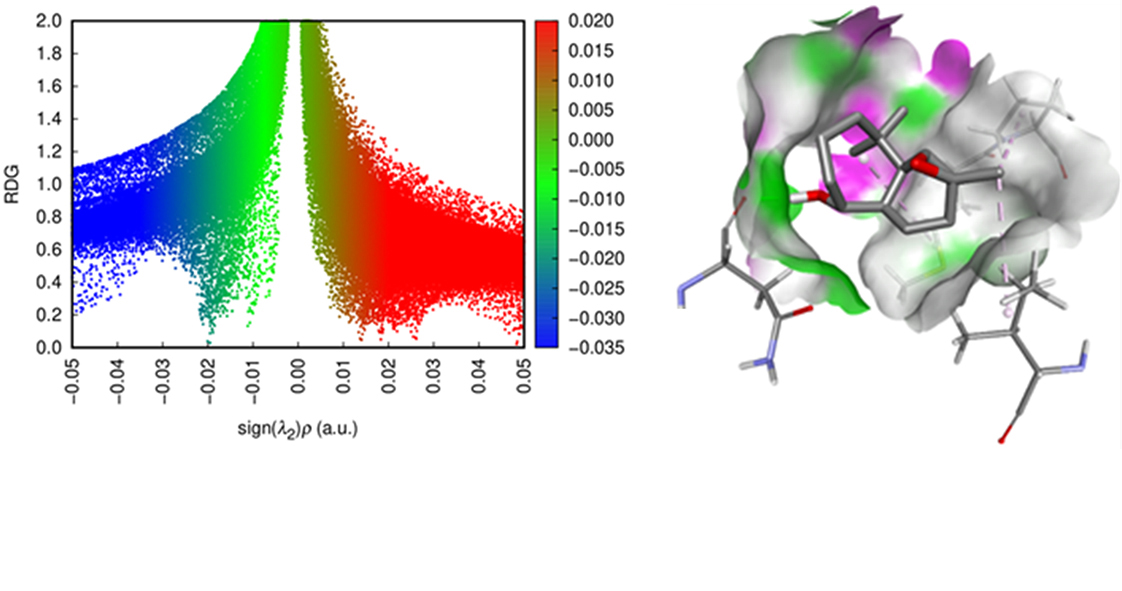
The stereoselectivity of the epoxidation reactions of cis-himachalone and cis-himachalol was investigated using theoretical approaches. Density functional theory calculations at the WB97XD/6-311G(d,p) level were employed to analyze chemical reactivity, utilizing reactivity indices within the framework of conceptual density functional theory. This analysis predicts that m-CPBA acts as an electrophile, while cis-himachalone and cis-himachalol function as nucleophiles. Examination of the energies associated with different reaction pathways indicates that the epoxidation reactions exhibit stereoselectivity. Additionally, molecular docking was conducted to target the catalytic domain of the Gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus topoisomerase IV enzyme, demonstrating that tested compounds possess favorable binding affinities compared to novobiocin. To assess the stability and structural characteristics of the protein–ligand complexes, 100-ns molecular dynamics simulations were performed. After analyzing several key parameters, including RMSD, RMSF, Rg, and the number of hydrogen bonds, it was found that tested compounds maintained stable protein conformations similar to those of the reference compound, suggesting their potential as effective inhibitors of the Staphylococcus aureus topoisomerase IV enzyme.