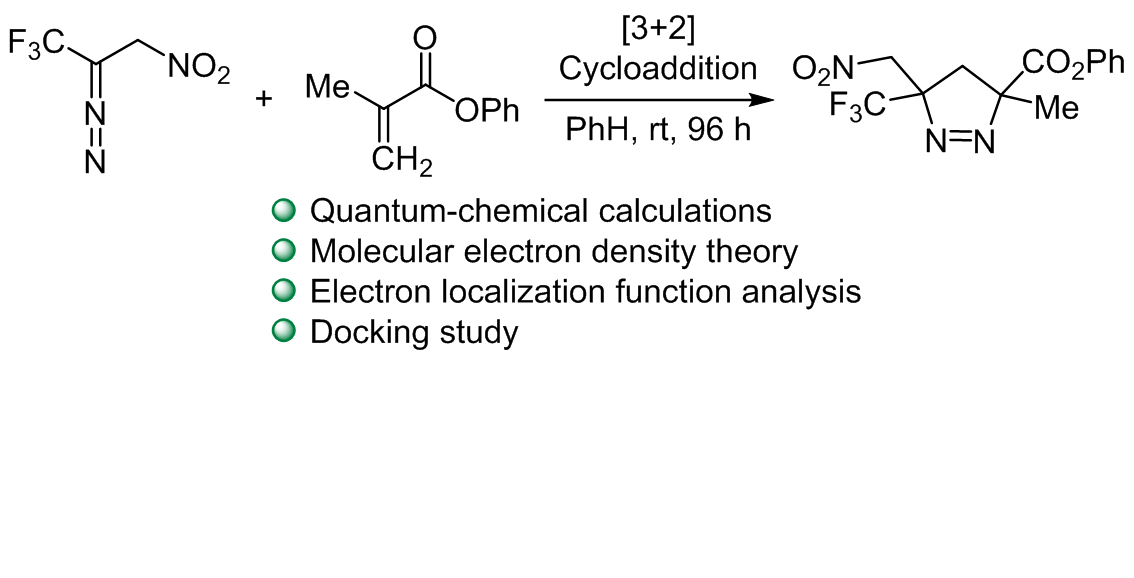Investigating the chemical reactivity and molecular docking of 2-diazo-3,3,3-trifluoro-1-nitropropane with phenyl methacrylate using computational methods
Ключевые слова:
[3+2] cycloaddition reaction, electron localization function topological analysis, global electron density transfer, quantum-chemical calculationsАннотация
The study utilized the molecular electron density theory to investigate the activation energies, reaction energies, and reactivity indices of the [3+2] cycloaddition reaction between 2-diazo-3,3,3-trifluoro-1-nitropropane and phenyl methacrylate. Employing electron localization function topological analysis, the molecular mechanism of the reaction was elucidated. Interestingly, the intended formation of the two single bonds does not occur simultaneously in this process. The initial step involves the formation of C2–C5 single bond, which is a prerequisite for subsequent reactions. Only after the formation of this single bond, the formation of the second C1–N3 single bond starts. This sequential bond formation sheds light on the intricate steps involved in the [3+2] cycloaddition reaction, providing a deeper understanding of its mechanism. Furthermore, a docking study conducted on the products under review uncovered significant insights. Specifically, the oxygen and nitrogen atoms within the molecules were found to enhance the interaction energy with proteins. This was exemplified by their interaction with the protease protein associated with COVID-19. The docking study not only contributes to the understanding of the products but also hints at potential bioactive properties, particularly in the context of protein interactions with crucial implications, such as those in the fight against viral infections and their impact on human health.